Introduction
The Spotify model was first introduced in 2012. Spotify model has emerged as a groundbreaking approach to organizational structure in the IT industry, offering a flexible and innovative framework for scaling agile practices. Developed by the music streaming giant Spotify, this model has gained significant attention for its ability to foster autonomy, collaboration, and rapid innovation within large-scale organizations[1][2].
This article provides an in-depth exploration of the Spotify model, its key components, implementation strategies, benefits, and comparisons with other agile frameworks. We will examine how this model addresses talent management, performance reviews, and organizational culture, as well as its applicability across various companies and industries.
The Core Components of the Spotify Model
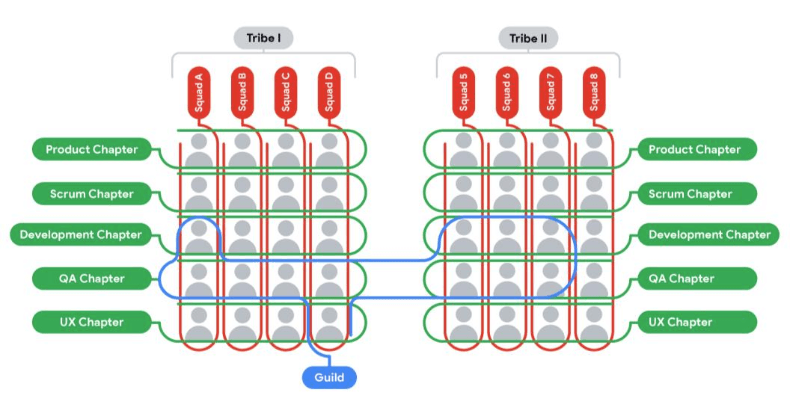
The Spotify model is built upon four primary organizational units: squads, tribes, chapters, and guilds. Each of these components plays a crucial role in creating a dynamic and adaptable structure that promotes both autonomy and alignment[1][2][4].
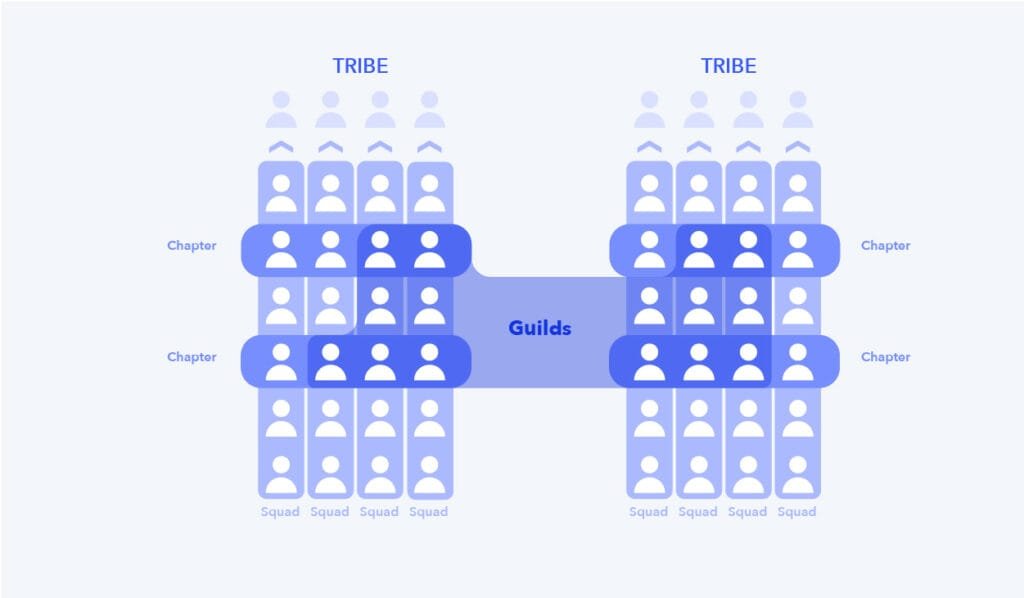
Squads
Squads are the fundamental building blocks of the Spotify model. They are small, cross-functional teams of 6-12 people who work together on specific features or components of the product[1][2]. Key characteristics of squads include:
- Autonomy: Squads have the freedom to choose their own agile methodologies and tools.
- End-to-end ownership: Each squad is responsible for a specific feature or component from conception to delivery.
- Long-term mission: Squads are organized around long-term missions rather than short-term projects.
Example: A “Search Experience” squad might be responsible for improving the search functionality within the Spotify app, including both frontend and backend components.
Tribes
Tribes are collections of related squads that work on similar areas of the product or business[1][2]. Typically consisting of 40-150 people, tribes provide a higher level of organization and coordination. Key aspects of tribes include:
- Shared business area: Squads within a tribe focus on related features or components.
- Tribe Leader: Each tribe has a leader responsible for providing the best possible environment for the squads.
- Regular gatherings: Tribes hold regular meetings to share knowledge and showcase work.
Example: A “Music Discovery” tribe might encompass several squads working on various aspects of music recommendation and exploration within the Spotify platform.
Chapters
Chapters are groups of individuals with similar skills or expertise who work across different squads within a tribe[1][2][11]. They serve as a mechanism for professional development and knowledge sharing. Key features of chapters include:
- Skill-based organization: Chapters bring together people with similar competencies.
- Regular meetings: Chapter members meet regularly to discuss challenges and share best practices.
- Line management: Chapter leads often serve as line managers for chapter members.
Example: A “Backend Engineering” chapter might include backend developers from various squads within a tribe, focusing on sharing knowledge about backend technologies and best practices.
Guilds
Guilds are voluntary, interest-based groups that span across the entire organization[1][2][12]. They provide a platform for employees to connect with others who share similar interests or passions, regardless of their squad or tribe affiliation. Key aspects of guilds include:
- Cross-organizational reach: Guilds can include members from any part of the company.
- Informal structure: Guilds are self-organized and voluntary.
- Knowledge sharing: Guilds facilitate the exchange of ideas and best practices across the organization.
Example: A “Machine Learning” guild might bring together data scientists, engineers, and product managers from various tribes who are interested in applying machine learning techniques to improve the Spotify product.
Implementing the Spotify Model from Scratch
Implementing the Spotify model requires careful planning and a commitment to cultural change. Here are the key steps to consider when adopting this framework:
- Assess organizational readiness: Evaluate your current structure and culture to determine if they align with the principles of the Spotify model.
- Define squads and tribes: Identify logical groupings of work and organize teams into squads and tribes based on product areas or business objectives.
- Establish chapters: Create chapters based on skill sets and competencies that span across squads.
- Encourage guild formation: Foster an environment where employees can form guilds around shared interests.
- Develop new leadership roles: Define and implement roles such as Product Owner, Agile Coach, and Tribe Lead.
- Promote autonomy and alignment: Empower squads to make decisions while ensuring alignment with overall company goals.
- Implement continuous improvement practices: Encourage regular retrospectives and feedback loops to refine the model over time.
- Invest in communication tools: Provide the necessary infrastructure for effective collaboration across squads, tribes, and chapters.
- Train and educate employees: Offer training programs to help staff understand and embrace the new organizational structure.
- Monitor and adjust: Regularly assess the effectiveness of the model and make adjustments as needed.
Benefits of the Spotify Model
The Spotify model offers numerous advantages for organizations seeking to improve agility, innovation, and employee satisfaction[2][4]:
- Increased autonomy: Squads have the freedom to make decisions and choose their own working methods, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility.
- Enhanced collaboration: The model promotes cross-functional teamwork and knowledge sharing through chapters and guilds.
- Faster innovation: Autonomous squads can experiment and iterate quickly, leading to more rapid innovation.
- Improved scalability: The model provides a flexible framework for scaling agile practices across large organizations.
- Better alignment: Despite the autonomy given to squads, the model ensures alignment through tribes and overall company objectives.
- Increased employee satisfaction: The focus on autonomy and skill development often leads to higher job satisfaction and retention.
- Adaptability: The model allows for quick reorganization and reprioritization in response to changing market conditions.
- Reduced silos: Chapters and guilds help break down organizational silos by promoting cross-team collaboration.
- Continuous learning: The emphasis on knowledge sharing and skill development fosters a culture of continuous learning.
- Improved product quality: End-to-end ownership by squads often results in higher quality products and features.
People and Talent Management in the Spotify Model
The Spotify model places a strong emphasis on people and talent management, recognizing that empowered and engaged employees are crucial for success[5][6]. Key aspects of people management in this model include:
- Talent acquisition: Focus on hiring individuals who thrive in autonomous, collaborative environments.
- Skill development: Encourage continuous learning and skill improvement through chapters and guilds.
- Career progression: Provide clear paths for both technical and leadership career advancement.
- Mentorship: Foster mentorship relationships within chapters and across the organization.
- Cross-functional experience: Encourage rotation between squads to broaden skills and perspectives.
- Autonomy and trust: Empower employees to make decisions and take ownership of their work.
- Work-life balance: Promote a healthy work-life balance to maintain long-term productivity and satisfaction.
- Diversity and inclusion: Emphasize the importance of diverse perspectives and inclusive practices.
- Recognition and rewards: Implement systems to recognize and reward both individual and team achievements.
- Feedback culture: Foster a culture of open and constructive feedback to drive continuous improvement.
Performance Reviews in the Spotify Model
Performance reviews in the Spotify model differ from traditional approaches, focusing on continuous feedback and development rather than annual evaluations[5][6]. Key elements of performance management in this model include:
- Continuous feedback: Encourage regular, informal feedback between team members and leaders.
- Self-reflection: Promote self-assessment and personal goal-setting.
- Peer feedback: Incorporate feedback from squad members and collaborators across the organization.
- Skill-based evaluation: Assess performance based on skill development and contribution to team goals.
- Alignment with company objectives: Ensure individual goals align with squad, tribe, and company objectives.
- Focus on growth: Emphasize personal and professional development over rigid performance metrics.
- Decoupled compensation: Separate performance discussions from salary negotiations to promote more open dialogue.
- Regular check-ins: Conduct frequent one-on-one meetings between employees and their chapter leads.
- Team-based assessments: Include squad-level performance evaluations to promote collective responsibility.
- Adaptable goals: Allow for flexible goal-setting and adjustment in response to changing priorities.
Comparison with Other Agile Models
While the Spotify model has gained significant attention, it’s important to compare it with other agile frameworks to understand its unique features and potential advantages[7][13]:
Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe)
SAFe is a comprehensive framework for scaling agile practices across large organizations. Compared to the Spotify model:
- Structure: SAFe provides a more structured approach with predefined roles and ceremonies, while the Spotify model offers greater flexibility.
- Scalability: SAFe is designed for very large enterprises, whereas the Spotify model may be more suitable for medium to large organizations.
- Implementation: SAFe requires a more formal implementation process, while the Spotify model allows for gradual adoption.
Scrum of Scrums
Scrum of Scrums is a scaling technique that coordinates multiple Scrum teams. In comparison to the Spotify model:
- Focus: Scrum of Scrums primarily addresses coordination between teams, while the Spotify model provides a comprehensive organizational structure.
- Flexibility: The Spotify model offers more flexibility in team structure and practices than Scrum of Scrums.
- Culture: The Spotify model places a stronger emphasis on organizational culture and autonomy.
Large-Scale Scrum (LeSS)
LeSS is a framework for scaling Scrum to large product development efforts. Compared to the Spotify model:
- Scope: LeSS focuses primarily on product development, while the Spotify model addresses overall organizational structure.
- Team structure: LeSS maintains a more traditional Scrum team structure, whereas the Spotify model introduces unique concepts like chapters and guilds.
- Adoption: LeSS provides a more prescriptive approach to adoption, while the Spotify model allows for more organic growth.
Disciplined Agile Delivery (DAD)
DAD is a process decision framework that provides a flexible approach to agile software delivery. In comparison to the Spotify model:
- Flexibility: Both models emphasize flexibility, but DAD provides more guidance on process selection.
- Scope: DAD focuses on the entire software delivery lifecycle, while the Spotify model addresses organizational structure more broadly.
- Roles: DAD defines more traditional agile roles, whereas the Spotify model introduces unique roles like chapter leads and tribe leaders.
Companies Implementing the Spotify Model
While the Spotify model was developed by and for Spotify, several other companies have adapted and implemented aspects of this framework[2][10]:
- ING Bank: The Dutch bank has implemented a version of the Spotify model to improve agility and innovation in its IT department.
- Siemens: The German conglomerate has adopted elements of the Spotify model in its healthcare division to enhance collaboration and speed up product development.
- Lego: The toy company has incorporated aspects of the Spotify model to improve its digital product development processes.
- Airbnb: The online marketplace has adapted elements of the Spotify model to organize its engineering teams.
- Netflix: While not directly implementing the Spotify model, Netflix has adopted similar principles of autonomy and alignment in its organizational structure.
- Klarna: The Swedish fintech company has implemented a version of the Spotify model to scale its engineering organization.
- Zalando: The German e-commerce company has adapted the Spotify model to organize its technology teams.
- Revolut: The digital banking company has incorporated elements of the Spotify model in its engineering organization.
- Skyscanner: The travel search engine has implemented aspects of the Spotify model to improve agility and innovation.
- Ericsson: The telecommunications company has adopted elements of the Spotify model in some of its development units.
Success Stories and Case Studies
Several companies have reported significant improvements after implementing aspects of the Spotify model:
ING Bank
ING Bank’s adoption of the Spotify model led to:
- 30% reduction in time-to-market for new features
- Improved employee satisfaction and engagement
- Enhanced collaboration between business and IT teams
Siemens Healthcare
Siemens Healthcare reported the following benefits:
- 50% reduction in development cycle time
- Increased innovation output
- Improved cross-functional collaboration
Lego Digital Solutions
Lego’s implementation of the Spotify model resulted in:
- Faster delivery of digital products and features
- Improved alignment between business strategy and technology development
- Enhanced employee satisfaction and retention
Challenges and Considerations
While the Spotify model offers numerous benefits, organizations should be aware of potential challenges:
- Cultural shift: Implementing the model requires a significant cultural change, which can be challenging for traditional organizations.
- Scalability: As organizations grow, maintaining the principles of autonomy and alignment can become more difficult.
- Coordination: Ensuring effective coordination between squads and tribes can be challenging, especially for complex products.
- Skill imbalances: The chapter structure may lead to skill imbalances across squads if not managed carefully.
- Leadership adaptation: Traditional managers may struggle to adapt to the new leadership roles required by the model.
- Measuring success: Defining and measuring success metrics can be more complex in this flexible structure.
- Regulatory compliance: Highly regulated industries may face challenges in implementing the full autonomy advocated by the model.
- Tool selection: Choosing and implementing the right tools to support collaboration across squads and tribes can be complex.
- Resistance to change: Employees accustomed to traditional hierarchies may resist the shift to a more fluid structure.
- Maintaining alignment: Ensuring all squads remain aligned with overall company objectives can be challenging as the organization scales.
Engineering, Data, Development, and Architecture Team Alignment
The Spotify Model can be applied to various IT functions:
Engineering teams:
- Squads: Feature-specific development teams
- Tribe: Overall product engineering
- Chapter: Programming language or technology-specific groups
- Guild: Software architecture interest group
Data teams:
- Squads: Data pipeline development, data analysis, machine learning
- Tribe: Data and analytics
- Chapter: Data engineering, data science
- Guild: Big data technologies interest group
Development teams:
- Squads: Front-end, back-end, mobile app development
- Tribe: Platform development
- Chapter: DevOps, quality assurance
- Guild: Agile methodologies interest group
Architecture teams:
- Squads: Microservices design, API development, system integration
- Tribe: Enterprise architecture
- Chapter: Solution architects, security architects
- Guild: Cloud computing interest group
Conclusion
The Spotify model represents a innovative approach to organizing IT and product development teams, offering a flexible and scalable framework for implementing agile practices at scale. By emphasizing autonomy, collaboration, and continuous improvement, this model has the potential to drive innovation, improve employee satisfaction, and enhance organizational agility.
While not without its challenges, the Spotify model has demonstrated significant benefits for companies willing to embrace its principles. As organizations continue to seek ways to adapt to rapidly changing market conditions and technological landscapes, the Spotify model offers a compelling alternative to traditional hierarchical structures and more rigid agile frameworks.
Ultimately, the success of the Spotify model depends on an organization’s ability to embrace its core principles of autonomy, alignment, and continuous improvement. By fostering a culture that values these principles and adapting the model to fit their unique needs, companies can leverage the power of this innovative approach to drive success in the digital age.
References
- Kniberg, H., & Ivarsson, A. (2012). Scaling Agile @ Spotify. Retrieved from https://blog.crisp.se/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/SpotifyScaling.pdf
- The Ingentis Blog. (2023). Organization design reimagined: The Spotify model. Retrieved from https://www.ingentis.com/blog/spotify-model/
- Atlassian. (n.d.). The Spotify Model for Scaling Agile. Retrieved from https://www.atlassian.com/agile/agile-at-scale/spotify
- LinkedIn. (2024). The Spotify Model: A Path to Success for Software Companies. Retrieved from https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/spotify-model-path-success-software-companies-sepehr-safaei-enc6f
- Deel. (2024). A Deep Dive into Spotify’s Employee Performance Reviews. Retrieved from https://www.deel.com/blog/employee-performance-reviews-at-spotify/
- Harvard Business Review. (n.d.). How Spotify Balances Employee Autonomy and Accountability. Retrieved from https://hbr.org/2017/02/how-spotify-balances-employee-autonomy-and-accountability
- Parabol. (n.d.). Agile Frameworks: A Complete Overview. Retrieved from https://www.parabol.co/resources/agile-frameworks-guide/
- LinkedIn. (2024). Understanding the differences between SAFe, Scrum of Scrums, and the Spotify Model. Retrieved from https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/understanding-differences-between-safe-scrum-scrums-spotify-matefi
- AgileBox. (n.d.). Agile Success Stories: Learn from the Giants. Retrieved from https://agilebox.app/blog/agile-success-stories/
- ProjectWorx. (n.d.). The Spotify model: agile at scale in a Swedish success story. Retrieved from https://projectworx.eu/the-spotify-model-agile-at-scale-in-a-swedish-success-story/
- Product School. (2023). What Is The Spotify Model? Retrieved from https://productschool.com/blog/product-fundamentals/spotify-model-scaling-agile
- LaunchNotes. (2024). Decoding the Spotify Model for Agile Scaling. Retrieved from https://www.launchnotes.com/blog/decoding-the-spotify-

