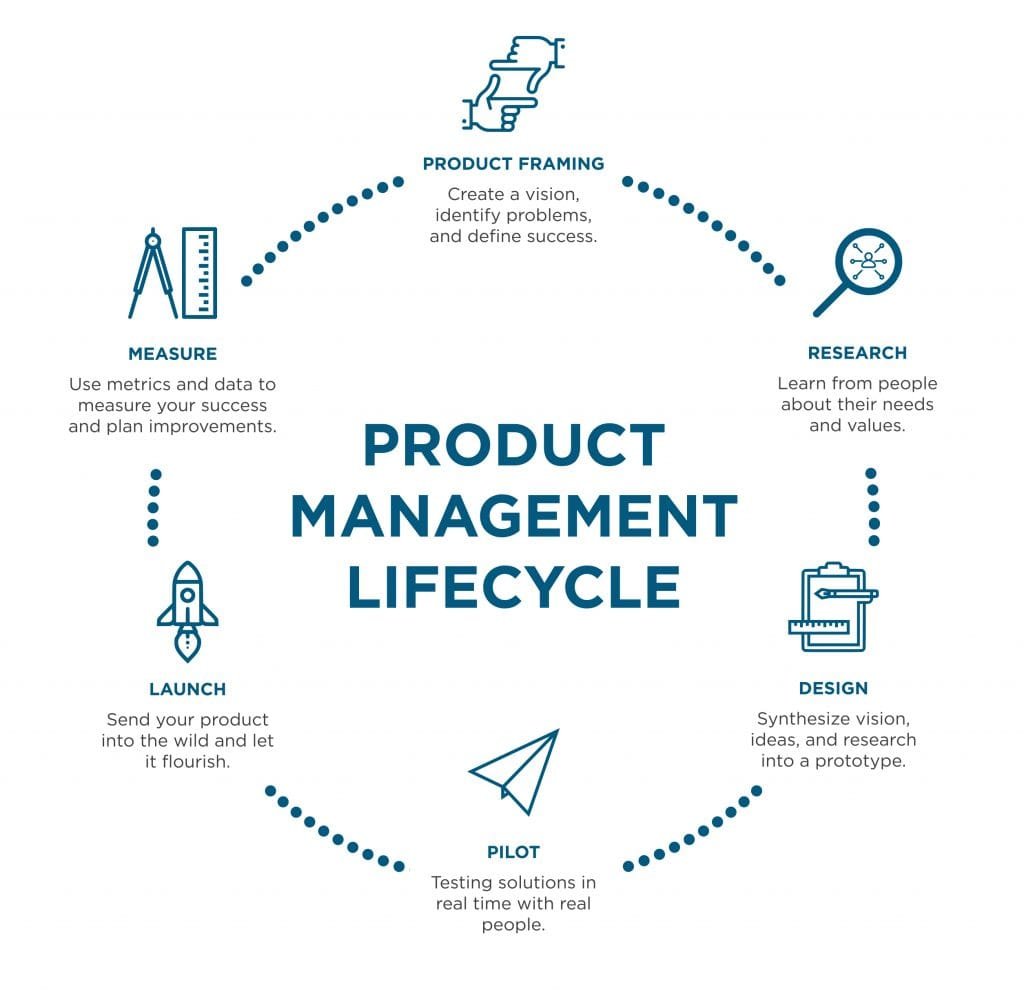
Understanding the Product Management Landscape
Product management is a critical function within organizations, serving as a bridge between various stakeholders, including customers, engineering, marketing, and sales teams. The role of a product manager (PM) encompasses the responsibility for defining the vision and direction of a product, ensuring that it aligns with both market needs and business goals. In the modern business environment, the strategic importance of product management cannot be overstated, as companies increasingly rely on innovative products to maintain competitive advantages.
At its core, product management revolves around understanding the value proposition offered by a product. This involves identifying customer pain points and needs, allowing PMs to define the problems that need to be addressed. By conducting market research and engaging with users, product managers can articulate the value proposition in a manner that resonates with their target audience. The process begins with clear problem definition, which lays the foundation for the development of viable solutions. In this regard, product managers must be effective communicators and facilitators, bringing together insights from various stakeholders to ensure that the product strategy is well-informed and targeted.
Furthermore, product managers play a pivotal role in the life cycle of a product from conception through launch and beyond. They are responsible for formulating the product strategy, prioritizing features, and ensuring that resources are allocated effectively. This necessitates a deep understanding of the market landscape, competitive products, and emerging trends, allowing PMs to make informed decisions that drive product success. The dynamic nature of markets also demands that product managers remain adaptable, adjusting strategies as necessary to respond to changing conditions and stakeholder feedback.
In essence, effective product management is about creating and communicating a compelling vision that aligns closely with customer needs and business objectives, positioning the organization for success in an ever-evolving landscape.
Navigating Roadmapping and KPIs
In the realm of product management, roadmapping holds a pivotal role in aligning product vision with execution. A product roadmap serves as a strategic tool that outlines the milestones, features, and timelines necessary for achieving the desired business objectives. Effective roadmapping not only provides a clear direction for the development team but also ensures that external stakeholders comprehend the product’s journey. Best practices for creating product roadmaps involve engaging cross-functional teams to gather insights, utilizing visual formats to enhance clarity, and maintaining flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions.
A well-constructed roadmap incorporates input from various departments, such as marketing, sales, and customer support. This collaborative approach fosters a comprehensive understanding of customer needs and market trends, ultimately leading to a more robust product offering. Prioritization is essential in the roadmapping process; thus, employing frameworks like the MoSCoW method (Must have, Should have, Could have, and Won’t have) can assist product managers in determining which features will deliver the most value to users while aligning with the overarching business strategy.
Alongside roadmapping, key performance indicators (KPIs) play a crucial role in assessing product success and guiding decision-making. KPIs offer quantifiable metrics that reflect the product’s performance against strategic goals. Common KPIs used in product management include customer acquisition cost (CAC), customer lifetime value (CLV), user engagement rates, and churn rate. Each of these indicators provides insight into different aspects of the product’s impact. For instance, monitoring customer engagement can inform product iterations and enhancements, ensuring that the development aligns with user expectations.
In conclusion, mastering the art of roadmapping and effectively utilizing KPIs ensures that product managers can navigate the complexities of product development while maintaining focus on achieving their strategic objectives. Clear communication and alignment through these tools foster a successful product management practice.
Agile Frameworks: Kanban and Scrum Ceremonies
Agile methodologies have become a cornerstone in product management, enabling teams to respond to change rapidly and effectively. Among these methodologies, Kanban and Scrum stand out as popular frameworks that promote streamlined processes and continual improvement within product development. Understanding the principles and practices associated with these frameworks is critical for product managers seeking to foster an environment conducive to innovation and delivery.
Kanban emphasizes visual management, where tasks are represented visually, often on a board that reflects the workflow. This approach allows teams to track progress and manage workloads effectively. By limiting work in progress (WIP), Kanban helps teams focus on the most critical tasks, thus enhancing overall efficiency. The continuous flow in Kanban enables teams to expedite delivery while adapting to stakeholder feedback instantaneously, which is vital in the fast-paced world of product development.
Conversely, Scrum operates on a time-boxed framework that divides the development process into manageable sprints, typically lasting two to four weeks. Scrum consists of several essential ceremonies: the Sprint Planning, the Daily Scrum, the Sprint Review, and the Sprint Retrospective. Each ceremony has a specific purpose—Sprint Planning aligns the team on goals for the upcoming sprint, while the Daily Scrum serves to discuss progress and impediments. The Sprint Review provides an opportunity for stakeholders to engage with the product increment, ensuring their feedback is integrated. Finally, the Sprint Retrospective focuses on reflecting upon the team’s processes, fostering continuous improvement.
Both Kanban and Scrum provide mechanisms that enhance team collaboration and ensure timely product delivery. By leveraging these agile frameworks, product managers can create a structured yet flexible environment that allows teams to stay aligned with stakeholder expectations and adapt to emerging project requirements, ultimately driving project success.
Cost Savings Through Scalable Frameworks and Automations
In today’s fast-paced business environment, organizations are continuously seeking ways to optimize their operations, and one effective approach is the implementation of scalable frameworks and automations. These strategies not only streamline processes but also lead to substantial cost savings in both time and resources. By harnessing scalable frameworks, teams can ensure that they have adaptable structures that grow alongside their projects, allowing for seamless scaling as needs evolve. This adaptability can significantly reduce operational overheads and the risk of resource wastage.
Automations play a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency within product management. By automating routine tasks such as data entry, reporting, and performance analysis, organizations minimize manual intervention which often contributes to errors and inefficiencies. Automations also free up valuable human resources, allowing teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than monotonous tasks. The end result is a more agile and responsive product management process that can adapt to changing market conditions without incurring significant additional costs.
An indispensable tool in this context is the use of dashboards that provide critical insights into performance and progress. These visual interfaces allow teams to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) in real-time, enabling quick decision-making based on actionable data. By integrating dashboards into their frameworks, organizations can track not only the success of automation strategies but also identify areas for further improvement, ensuring that ongoing maintenance becomes an integral part of the product management lifecycle. As such, dashboards contribute significantly to continuous improvement initiatives, further solidifying the cost-saving potential of scalable systems.
To maximize the benefits of these frameworks, organizations should invest in training and development to ensure that team members are proficient in using the automation tools and dashboards. Such investments reinforce the value of scalability and automation, ultimately leading to more sustainable and profitable product management practices.