‘Amazon Prime’ around the World for International Expansion, yet Faces Challenges from Alibaba, Flipkart and Others
It was not very long since Amazon has started its business as a book seller with aims to spread its footprints across the globe. This techie business now represents 44% of Ecommerce and 4% in retail. The business made 8000% high in stocks since it went to public in 1997 (Marc, 2018). Amazon is the leading business in many streams now offering various offers, schemes and proper business plans and is now setting out to grab the world. Prime was one of the biggest and successful programs in Amazon which brought many customers domestically and now bringing customers internationally. Prime concentrates more on delivering quick, music, videos, books and a lot. It was one of the successful programs in recent businesses.
Strategies: Acquisitions Vs. Investments
Amazon is now the leading business in North America and Europe, while Alibaba taking the lead in China, Southeast Asia (Singapore, Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines and so on). Both Companies competing each other to grab the international market as fast as they could and as more as they could as “Winning or Losing depends on who’s the fastest and smartest”. Both these companies are capitalizing on three things
- Increase internet and technology penetration to make business
- Digitize the global financial systems
- Making huge profits across the world
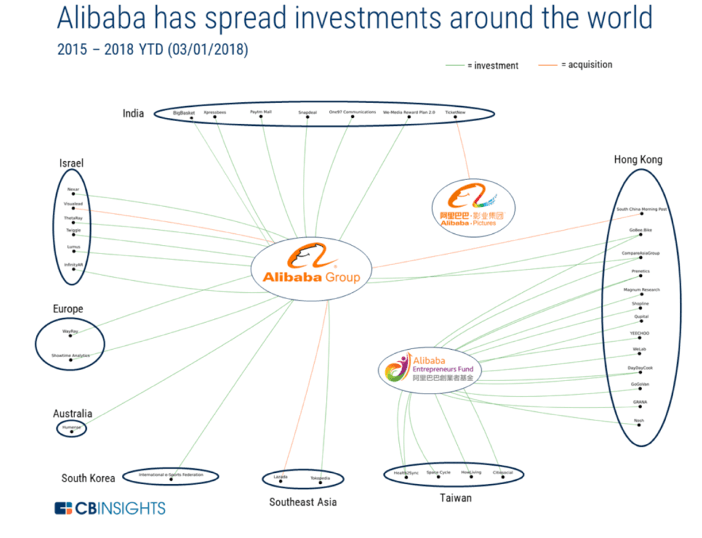
Alibaba and Amazon have approached these new opportunities with completely different ways — Amazon acquires whereas Alibaba invests. Outside the North American country and China, Alibaba has taken a minority stake in twice as many companies as Amazon, while Amazon has acquired 5X more companies than Alibaba.
While the businesses square measure following completely different ways for growth, their goal is ultimately the same — take their e-commerce and logistical expertise global.
Amazon is focused on globalizing its branded Marketplace, and will spend billions of dollars over the next decade to bring its model of low prices, vast selection, and fast delivery to the world. Alibaba is expanding its logistics network around the world and piecing together subsidiaries to connect the world’s e-commerce markets.
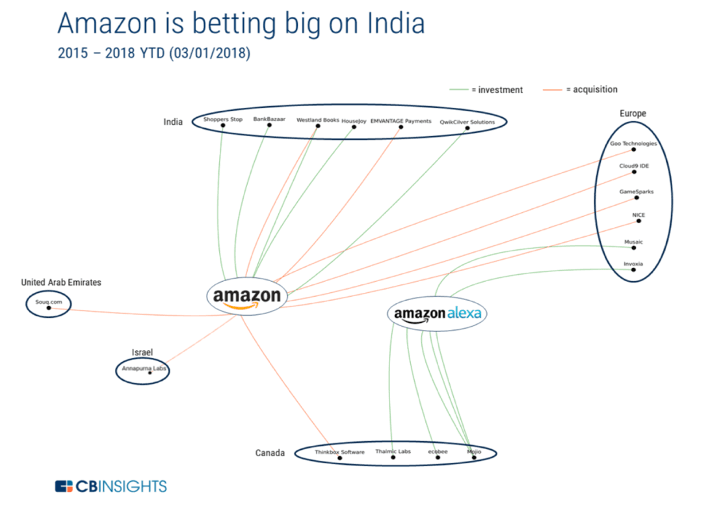
Amazon’s struggle to duplicate its US success overseas
The five key practices that any tech firms must adapt in order to make their international operations a successful venture (Alex, 2018). These practices are:
- Partnering with a local country’s brand with a strong name as method of entry.
- Adapting a meaningful, easily recognizable local country’s name.
- Hiring local leadership.
- Launching a separate service based locally in that country.
- Giving local operations autonomy to build their own business model and operate independent of US based headquarters.
Amazon acquired Joyo, the biggest online book seller in China, in 2004 and thus entered China market. Joyo was rebranded as Amazon China in 2011. As Amazon grew from an online book store to e-commerce juggernaut in the United States, it failed to recreate such success in China.
Amazon created several of identical mistakes that eBay created in China. Amazon tried to suit its operating business model within the U.S to China, but like eBay, the Chinese consumer market demanded something different. Like eBay, Amazon most well-liked economic process and wasn’t willing to relinquish a lot of autonomy to its China operations. There are conflicts of interests between the Chinese management team and Amazon headquarters in decision making, Amazon headquarters in Seattle tends to override the Chinese management’s decision.
Amazon might rule out the North American country, but it’s a very different story overseas. The company’s quarterly earnings on Feb. 1 (2019) showed US sales accelerating to $37 billion last quarter, a 42% increase from a year earlier. Overseas sales also rose to a record $18 billion last quarter, but quarterly growth rates were flat: 29% year-on-year, the same rate as the previous quarter. Amazon told company shareholders throughout a recent presentation that the majority of its international losses were because of significant investments in Indian subsidiaries.
On top of it Amazon is investing on “Home delivery and supply chain logistics”, “Artificial intelligence”, “Healthcare”, “Geographic expansion” and concentrating on “Price Sensitivity”, “Payment System”, “Market Entry by Acquisition” also trying to rectify it’s mistakes by “investigating on fake goods”, “going deeper into the Indian Online Retail Market”, “Announcing new International Shopping feature”, “Launching their first Debit Card in Mexico” and so on (CBInsights, 2018).
Global Expansion More Crucial for Amazon Than Alibaba
India and geographic region were known as core regions for “the next $5 trillion piece of land.” Nowark and his team (Will, 2018) noted that both Amazon and Alibaba have begun “planting seeds” in Latin America and Australia, adding that the U.S. giant is presently ahead in India whereas its Chinese rival has the lead in geographical region. However, the analysts conjointly warned that Amazon has additional riding on this costly battle for world e-commerce domination.
Also coming with different ideas like Amazon partnering with media and social platforms can suggest what products or brands a person is wearing and can take the customers to shop from the site and so on can make Amazon stay at the top. While Alibaba is spending most of its money on different companies as investments and Amazon investing in acquisitions it still depends on who’s strongest and who’s the smartest to win in this race.
